Webservices
Web services and APIs are two of those overlapping tech terms that regularly get confused. You might have even heard these words used interchangeably, but are they even the same thing?
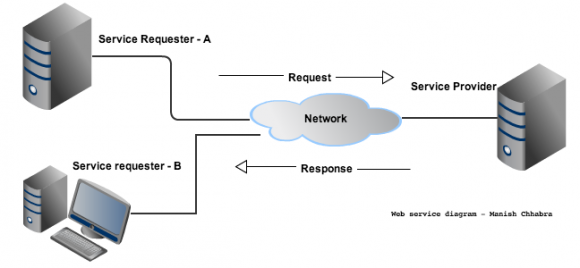
Web Services take Web-applications to the Next Level. By using Web services, your application can publish its function or message to the rest of the world. Web services use XML to code and to decode data, and SOAP to transport it (using open protocols).
While they do have some overlap, web services and APIs are two different concepts. If you need a quick and simple explanation, we’ve got you covered. In previous articles, we broke down the difference between microservices and APIs, SDKs and APIs, and today we’ll do the same for web services and APIs!
Webservices In Java
- Contact Web Services 730 Rivers Street 116 Edwin Duncan Hall ASU Box 32134 Boone, NC 28608 Email us.
- © 2015 CompSource Mutual Workers' Compensation Insurance (800) 347-3863.
- Web services is a standardized way or medium to propagate communication between the client and server applications on the World Wide Web. This course will give a detailed insight into various components of web services like SOAP,WSDL, REST, and how they operate.
- Based in Chattanooga, Alliance Web Services has helped businesses across the nation build and improve their online marketing efforts. Our clients consistently see an increase in traffic to their business. We also maintain an open line of communication to keep clients informed of.
What Is an API?
The term “API” stands for Application Programming Interface. If you break that down word by word, you can get a pretty good grasp of what it means. An API is an interface that can be used to program software that interacts with an existing application. In practice, an API is “a set of functions and procedures” that allow you to access and build upon the data and functionality of an existing application.
“APIs have been described as the glue holding the Internet together. They are woven into the fabric of most things end users do on their devices. Ever wonder how you can play Spotify from within an Uber? APIs enable two otherwise distanced entities to talk to each other in a more standardized format.” – What is an API?, Nordic APIs
APIs have been around for donkey’s years. Pretty soon after the first computer application was created, clever developers realized that you could get a lot more out of distinct applications by linking them together — and so the API was born.
Nowadays, when we’re talking about APIs we’re typically referring to web APIs, which expose an application’s data and functionality over the internet. If you look closely, you’ll see that web APIs power our everyday lives:
- When you log into a website using your Facebook profile
- When you switch on Netflix and see dozens of new movies flood the screen
- When you look for flights on Google
… and the list goes on and on
Technically speaking, web APIs usually send data back and forth using HTTP requests. These requests often return textual data in the form of a JSON or XML response.
What Is a Web Service?
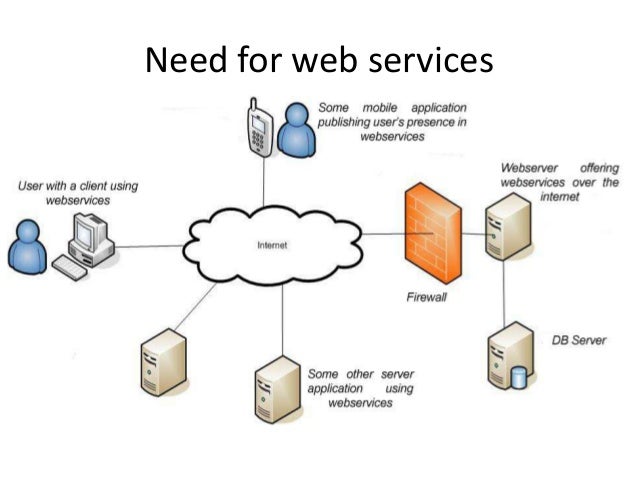
Simply put, a web service is a resource that’s made available over the internet. Therefore, web services, by definition, require a network. The term “web service” is defined by W3C (the World Wide Web Consortium) and so it technically follows a whole host of standards.
A Web service is a software system designed to support interoperable machine-to-machine interaction over a network. It has an interface described in a machine-processable format (specifically WSDL). Other systems interact with the Web service in a manner prescribed by its description using SOAP-messages, typically conveyed using HTTP with an XML serialization in conjunction with other Web-related standards.
As far as many developers are concerned, web services mostly use SOAP — a messaging protocol where XML data is shared via HTTP requests. Others disagree with this, saying that web services don’t have to use SOAP, but it’s an issue of semantics more than anything else.
Finally, web services are usually associated with Service Oriented Architecture. Service Oriented Architecture, or SOA, is an architectural pattern for designing software applications where features are split up and made available as services in a network.
APIs vs Web Services
Contrary to what you might think, APIs and web services are not mutually exclusive. In fact, one is a subset of the other: every web service is an API — since it exposes an application’s data and/or functionality — but not every API is a web service. This is because the definition of a web service is quite restrictive when it comes to implementation:
- Web services require a network. While APIs can be on- or offline, web services must use a network.
- APIs are protocol agnostic. While APIs can use any protocols or design styles, web services usually use SOAP (but sometimes REST, UDDI, and XML-RPC).
There’s another big distinction. Many public APIs are transparent, with open documentation and self-service portals for quick developer onboarding. That’s because the point of many modern day APIs is, after all, to facilitate interaction with an application. On the other hand, web services have not enjoyed such an open history: instead, they tend to offer specific data and/or functionality to specific partners — they’re not there to be hacked about with.
SOA Gave Web Services a Bad Name
For developers for whom web services necessarily mean SOA, there’s one big issue with web services. In Service Oriented Architecture, the services have to be designed in anticipation of how they’ll ultimately be used and who will be using them. If there’s a lack of proper planning, or if needs change just with the passing of time, developers can quickly find themselves stringing together a mishmash of services to build the right implementation.

Inherently, web services don’t have this problem. It’s only when web services are used in a Service Oriented Architecture that these issues can pop up. In truth, then, SOA has given web services a bit of a bad name.
Final Thoughts
There you have it: an API is an interface that allows you to build on the data and functionality of another application, while a web service is a network-based resource that fulfills a specific task. Yes, there’s overlap between the two: all web services are APIs, but not all APIs are web services.
Both web services and APIs are — at their core — very useful and very much used today. However, it’s the web services associated with SOAP and/or Service Oriented Architecture which are falling out of favor.
Web services and APIs are two of those overlapping tech terms that regularly get confused. You might have even heard these words used interchangeably, but are they even the same thing?
While they do have some overlap, web services and APIs are two different concepts. If you need a quick and simple explanation, we’ve got you covered. In previous articles, we broke down the difference between microservices and APIs, SDKs and APIs, and today we’ll do the same for web services and APIs!
What Is an API?
The term “API” stands for Application Programming Interface. If you break that down word by word, you can get a pretty good grasp of what it means. An API is an interface that can be used to program software that interacts with an existing application. In practice, an API is “a set of functions and procedures” that allow you to access and build upon the data and functionality of an existing application.
“APIs have been described as the glue holding the Internet together. They are woven into the fabric of most things end users do on their devices. Ever wonder how you can play Spotify from within an Uber? APIs enable two otherwise distanced entities to talk to each other in a more standardized format.” – What is an API?, Nordic APIs
APIs have been around for donkey’s years. Pretty soon after the first computer application was created, clever developers realized that you could get a lot more out of distinct applications by linking them together — and so the API was born.
Nowadays, when we’re talking about APIs we’re typically referring to web APIs, which expose an application’s data and functionality over the internet. If you look closely, you’ll see that web APIs power our everyday lives:
- When you log into a website using your Facebook profile
- When you switch on Netflix and see dozens of new movies flood the screen
- When you look for flights on Google
… and the list goes on and on
Technically speaking, web APIs usually send data back and forth using HTTP requests. These requests often return textual data in the form of a JSON or XML response.
What Is a Web Service?
Simply put, a web service is a resource that’s made available over the internet. Therefore, web services, by definition, require a network. The term “web service” is defined by W3C (the World Wide Web Consortium) and so it technically follows a whole host of standards.

A Web service is a software system designed to support interoperable machine-to-machine interaction over a network. It has an interface described in a machine-processable format (specifically WSDL). Other systems interact with the Web service in a manner prescribed by its description using SOAP-messages, typically conveyed using HTTP with an XML serialization in conjunction with other Web-related standards.
As far as many developers are concerned, web services mostly use SOAP — a messaging protocol where XML data is shared via HTTP requests. Others disagree with this, saying that web services don’t have to use SOAP, but it’s an issue of semantics more than anything else.
Finally, web services are usually associated with Service Oriented Architecture. Service Oriented Architecture, or SOA, is an architectural pattern for designing software applications where features are split up and made available as services in a network.
APIs vs Web Services
Contrary to what you might think, APIs and web services are not mutually exclusive. In fact, one is a subset of the other: every web service is an API — since it exposes an application’s data and/or functionality — but not every API is a web service. This is because the definition of a web service is quite restrictive when it comes to implementation:
- Web services require a network. While APIs can be on- or offline, web services must use a network.
- APIs are protocol agnostic. While APIs can use any protocols or design styles, web services usually use SOAP (but sometimes REST, UDDI, and XML-RPC).
There’s another big distinction. Many public APIs are transparent, with open documentation and self-service portals for quick developer onboarding. That’s because the point of many modern day APIs is, after all, to facilitate interaction with an application. On the other hand, web services have not enjoyed such an open history: instead, they tend to offer specific data and/or functionality to specific partners — they’re not there to be hacked about with.
SOA Gave Web Services a Bad Name
Webservices.ulm.edu
For developers for whom web services necessarily mean SOA, there’s one big issue with web services. In Service Oriented Architecture, the services have to be designed in anticipation of how they’ll ultimately be used and who will be using them. If there’s a lack of proper planning, or if needs change just with the passing of time, developers can quickly find themselves stringing together a mishmash of services to build the right implementation.
Inherently, web services don’t have this problem. It’s only when web services are used in a Service Oriented Architecture that these issues can pop up. In truth, then, SOA has given web services a bit of a bad name.
Final Thoughts
There you have it: an API is an interface that allows you to build on the data and functionality of another application, while a web service is a network-based resource that fulfills a specific task. Yes, there’s overlap between the two: all web services are APIs, but not all APIs are web services.
Both web services and APIs are — at their core — very useful and very much used today. However, it’s the web services associated with SOAP and/or Service Oriented Architecture which are falling out of favor.